Indian Constitution GK MCQs For All Competitive Exams
भारतीय संविधान से सम्बंधित बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न
Important solved multiple choice questions (MCQs) Based on Indian Constitution General Knowledge. These fully solved multiple choice questions (MCQs) Based on Indian Constitution General Knowledge are very helpful for better preparation of Exams like TET, CTET, JAO, UPSC, PSC, Clerk, Steno, TGT, HPPDC, HPSSC, Bank PO and SSC Exams.
Indian Constitution General Knowledge Solved MCQs
Indian Constitution GK asked in Previous competitive Exams | SET-56
Question : 1-10
Question: 1
Which pact abandoned the separate electorates for depressed classes?
Question: 2
In which of the session of Round Table Conferences, Congress participation was there?
Question: 3
The meeting of Indian and British political leaders during 1930–32 in London has often been referred to as the First, Second & Third Round Table Conferences. It would be incorrect to refer to them as such because: [1996]
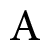 (the Indian National Congress did not take part in two of them
(the Indian National Congress did not take part in two of them
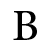 ( Indian parties other than the Indian National Congress, participating in the conference represented sectional interests and not the whole of India
( Indian parties other than the Indian National Congress, participating in the conference represented sectional interests and not the whole of India
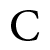 ( the British Labour Party had withdrawn from the conference thereby making the proceeding of the conference partisan
( the British Labour Party had withdrawn from the conference thereby making the proceeding of the conference partisan
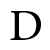 (It was an instance of a conference held in three sessions and not that of three separate conference
(It was an instance of a conference held in three sessions and not that of three separate conferenceQuestion: 4
The composition of the Constituent Assembly was:
Question: 5
Which association led the Civil Disobedience Movement in the North-West Frontier region?
Question: 6
Who attended all the three Round Table conferences?
Question: 7
The Poona Pact which was signed between the British Government and Mahatma Gandhi in 1934 provided for [1997]
 (creation of dominion status for India
(creation of dominion status for India
 ( separate electorates for the Muslims
( separate electorates for the Muslims
 ( The separate electorate for the Harijans
( The separate electorate for the Harijans
 (A joint electorate with the reservation for Harijans
(A joint electorate with the reservation for HarijansQuestion: 8
Question : 8The members of the Constituent Assembly were:
 Nominated by the Governor-General
Nominated by the Governor-General
 Directly elected by the people
Directly elected by the people
 Elected by the legislatures of various provinces and nominated by the rulers of the princely states
Elected by the legislatures of various provinces and nominated by the rulers of the princely states
 Nominated by the Congress and the Muslim League
Nominated by the Congress and the Muslim League
